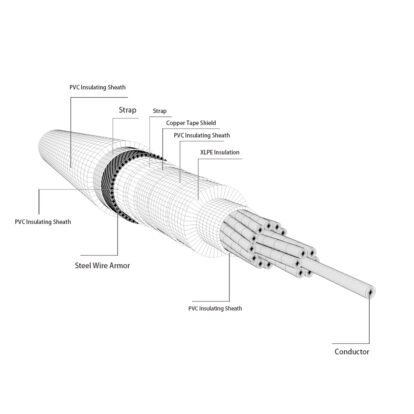
A bare wire is a wire with no insulation on its surface. It is mainly used in the manufacture of electric power, transportation, telecommunication engineering and electric motors, transformers and electrical appliances. In order to ensure the current and electrical safety in the direction of the wire, external insulation must be provided during installation, such as space spacing, insulator support, etc. Therefore, the product itself is not marked with "Using Voltage". The detection of bare wires and products can effectively help the research and development of conductive metal materials with high conductivity, high strength, high heat resistance, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, etc., as well as pressure processing of non-ferrous metals (hot rolling, cold drawing, twisting ) process technology and equipment, preparation of conductive alloys, research and process technology development of high-purity non-ferrous metal smelting and modification.
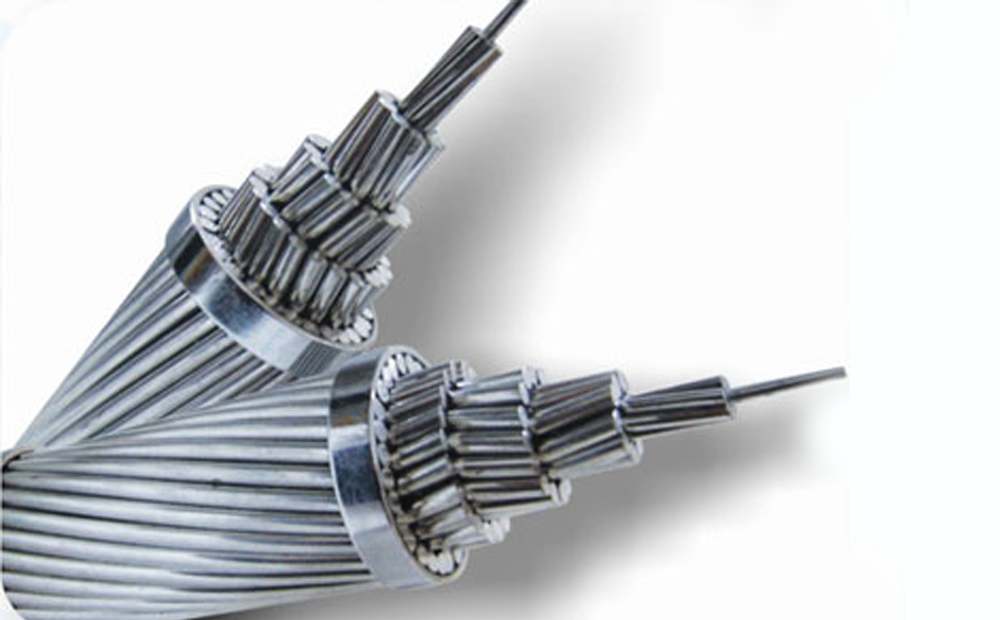

According to the product structure and application, the detection types of bare wires and their conductors are mainly divided into four categories: single wire, bare stranded wire, flexible wire and braided wire, shaped wire and profile. The following is the detailed detection and analysis knowledge of various bare wires and products.
Bare single wire detection and analysis
Bare single wires refer to non-ferrous metal single wires of different materials and sizes, which can be divided into round single wires (copper, aluminum and their alloys), flat wires (copper, aluminum and their alloys), single and double metal wires (aluminum-clad steel, copper-clad aluminum, copper-clad steel), with metal plating (tin, silver, nickel). Most of these products are used as materials in the production of wire and cable products.

Detection and analysis of bare stranded wire
1.Performance testing and analysis of bare stranded wire
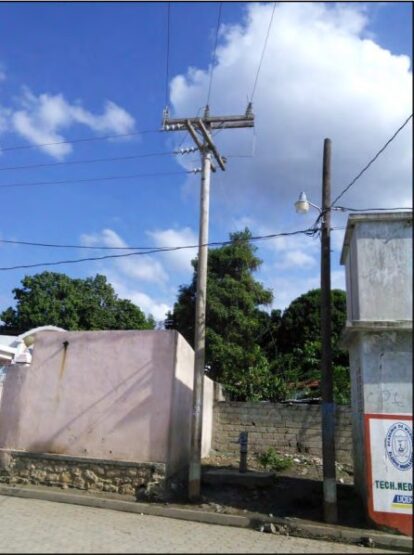
Bare stranded conductors are often called overhead conductors because they are always mounted on poles. Overhead conductors themselves have no rated voltage, i.e. the same series of conductors can be used from low voltage, medium voltage, high voltage or even extra high voltage. However, the 330-500kv class has special requirements on the outer diameter and surface finish of the wire to reduce the surface corona of the guide wire (that is, the electric field causes the local air around it to dissipate electricity, which will increase the wire loss). Although the structure of the overhead line is simple, its function is extremely important.
In the power grid, the line length accounts for more than 90% of the total, especially the 110kv-500kv high-voltage transmission and distribution lines account for the vast majority. According to the structure, the bare stranded wire detection category can be divided into three types. One is made of a single wire of a single metal material, such as aluminum stranded wire, copper stranded wire, aluminum alloy stranded wire, etc.; the other is steel stranded wire as the core wire to increase the tensile strength, and the outer stranded wire One layer of steel or aluminum stranded wire or several layers of aluminum wire or aluminum alloy wire; the third is bimetal single-wire stranded wire, such as aluminum-clad steel stranded wire. ACSR is the most widely used type of inspection. Since the steel core is subjected to the pulling force suspended on the rod, the distance between the rods can be increased, the investment can be reduced (especially the high-voltage wire), the service life of the wire can be extended, and the safety can be improved. If there is corrosive gas around the laying line (such as salt spray in the seaside or chemical plant area), anti-corrosion steel-cored aluminum strands coated with anti-corrosion coating should be used.
2. Analysis on improvement of bare stranded wire detection index
(1) Increase the tensile strength and vibration resistance without increasing the weight of the conductor, such as high-strength aluminum alloy stranded wire, self-damping (anti-vibration) wire, etc.;
(2) Long-term working temperature or conductivity to increase transmission capacity, such as dual-capacity detection indicators, etc.
(3) In cold areas, to prevent the surface of the wire from freezing, the wire can improve its anti-ice and snow performance

Detection and analysis of flexible wiring and braided wire
There are many types of flexible wiring and braided wires, but the amount is small; such as motor brush wires, battery parallel wires, antennas, grounding wires and shielding nets, etc. Such products are bundled and twisted with thin copper single wires; battery parallel wires are usually made into flat shapes (commonly known as scorpion wires); shielding mesh sleeves are prepared and placed outside the wires that need to be shielded.
Detection and analysis of molded lines and profiles
The cross-sectional shapes of bare wires are different, and the ones that are not round are generally called profiled wires, and the wire products that are not used in larger lengths are called profiled wires.
Here bare wires and products can be divided into three detection types according to their usage:
1. Used as copper and aluminum row materials for detection and analysis of high-current busbars (also known as busbars)
Most of them are flat, and they are also made of hollow rectangles and half-bows. It is used for power transmission in power plants and substations; in switchgear. Insulated busbars with insulating layers have been developed in recent years.
2. Detection and analysis of conductors for catenary
These wires are used in overhead railways such as electrified railways, city trams and electric vehicles in tunnels (such as subways, underground tunnels). Due to the large-scale development of urban rail transit lines and electrified railways, the use of contact network conductors (often called trolley lines, now called contact lines) has multiplied. In addition to good electrical conductivity, sufficient tensile strength and good weather resistance, excellent wear resistance is also important and directly related to service life.

3. Detection and analysis of special-shaped row materials
Mainly used for commutator parts of various types of motors, as well as various switches and cutter heads. The cross-sectional shape is trapezoidal, single peak, double peak, made of copper or copper alloy.