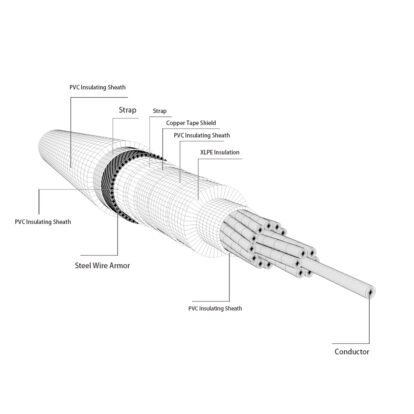
In recent years, we have found that the copper conductors of cable products will be oxidized and blackened every summer, which seriously affects the electrical conductivity of the cables. After the conductor is oxidized and blackened, the cable cannot continue to be used, resulting in scrapping, which brings great losses to users and production enterprises.

Causes of Copper Conductor Oxidation
In order to reduce the oxidation of conductors in semi-finished and finished cables, provide qualified products for delivery to users, and maximize the satisfaction of market requirements, we have analyzed the reasons for the oxidation and blackening of copper conductors in cables. According to our long-term experience in wire and cable production, the main reasons for the oxidation and blackening of copper conductors are as follows:
- The quality of the copper itself is not good, and there are many impurities.
- Copper wire forms oxidation during wire drawing.
- The stranded copper conductor forms oxidation after exposing in the air for a long time.
- During the production process, when entering the water tank for cooling, improper process control will cause moisture to enter the conductor and cause oxidation.
- If it is not sealed during storage, the copper conductor is easy to oxidize after contacting the water vapor in the hot and humid air in summer.
- During use,the user does not seal the cable after it is segmented and make it exposed to the air for a long time to cause oxidation.
In order to thoroughly investigate other unexplained reasons for conductor oxidation and blackening, we specially take samples and send them to the Mechanical Industry Electrical Materials and Special Cable Products Quality Supervision and Inspection Center for testing and analysis.The copper conductor and insulating material in the sample were tested separately by ICP elemental analysis method, and those potential elements that caused the blackening of the copper conductor were not detected from the copper conductor in the sample, which indicated that there is no impurity that easily lead to blackening in the copper conductor itself.While 0.04% S and 2.7% Pb were detected in the insulating material in the sample.The existence of these substances is a potential factor that causes the blackening of copper conductors.
In order to further analyze and confirm whether the blackening substance of the copper conductor is copper oxide, we conducted a dilute hydrochloric acid dissolution experiment on the copper conductor of the sample cable.First put the copper conductor into dilute hydrochloric acid solution (the volume ratio of hydrochloric acid to water is 1:1), and it is found that the blackened substance on the surface of the copper conductor is quickly eliminated (copper sulfide is not easily soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid), and the solution is transparent and light blue , so it can be preliminarily judged that the blackened substance on the surface of the copper conductor is copper oxide.
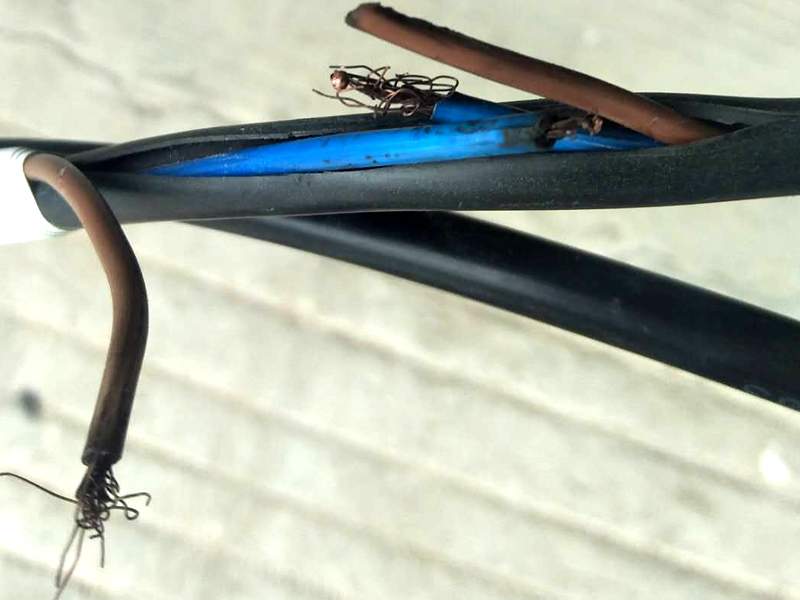

In summary, the blackened substance on the surface of the copper conductor of the sample cable submitted for inspection was analyzed and detected to be copper oxide; the OH group in the insulating material makes it weakly acidic, and the copper conductor is particularly prone to blackening in this environment. CL in the insulating material is also easy to blacken the copper conductor in direct contact with it. In addition, the presence of Pb and trace amounts of S in insulating materials may also cause blackening of copper conductors.
Solutions for oxidation of copper conductors
In order to fundamentally prevent the oxidation and blackening of copper conductors in the semi-finished and finished products of wire and cable, the production process of wire and cable should be controlled, and the semi-finished and finished products should be kept properly, including the following measures:

- For the oxidation and blackening of copper conductors caused by the poor quality of copper itself and many impurities, it should be tested strictly according to the standard requirements when the raw copper rods enter the factory, and the impurity components should be analyzed to ensure that the impurity content of the raw copper rods is within the range specified in the GB/T3952-2008 standard, or the copper content is higher than the standard requirement.
- For the oxidation and blackening of the copper rod during the wire drawing process, long-term contact with the wire drawing lubricant and the copper wire during the wire drawing process should be avoided.
- For the oxidation and blackening of stranded copper conductors caused by long-term exposure to air, the storage time of stranded copper conductors should be shortened as much as possible, and the transfer to the next process (such as refractory mica tape wrapping or insulation extrusion, etc.) should be accelerated to prevent the copper conductor from being in contact with air for a long time.Oxygen in the air contacts with copper to form copper oxide. Slight oxidation will cause redness, and severe oxidation will cause purple. If it must be stored for a long time, the copper surface can be wrapped with appropriate materials (such as plastic film).
- In the production process, due to improper process control when entering the water tank for cooling, resulting in moisture entering the conductor and causing oxidation and blackening, the production skills and responsibility of the operator should be improved to ensure that it is strictly controlled when the extruder extrudes the insulation according to the mature process and the conductors at both ends are strictly prohibited from entering water.
- For unsealed terminals during storage, copper conductors are prone to oxidation and blackening after contact with moisture in the hot and humid air in southern summer. It should be ensured that the finished wires and cables after production are immediately taken appropriate measures (for example, cable manufacturers in the industry often Use the cable sealing cap) to seal both ends. If the sealing cap is found to be damaged during storage, it should be resealed immediately.
- If the purchased cable is not sealed after being segmented by the user during use, and it is exposed to the air for a long time to cause oxidation and blackening, the user should be informed in advance that the seals at both ends of the cable will not be cut temporarily during the cable laying process when the cable is delivered to the user.The sealing cap can only be opened after all laying is completed, and the cable terminal should be made in time to prevent the copper conductor of the cable terminal from being oxidized when in contact with air for a long time.When the cable is laid in sections, the two ends of the sectioned cable must be sealed in time.If the two ends of cables can not be sealed by calbe caps on construction site, materials such as insulating tape can be used to prevent the copper conductor of the cable from being exposed to the air for a long time to form oxidation.
Conclusion:
In view of the oxidation of wire and cable conductors, only by finding out the main root cause and verifying the corresponding improvement plan through practice, can we bring real and effective economic benefits to the production enterprises.