Installation methods for low-voltage cables have a significant impact on their reliability and safety. Choosing a reasonable method for laying low-voltage cables can greatly reduce the cost of cable construction. In the construction of cable entry into the ground, it is necessary to combine practical examples of construction cases to plan the cable laying method reasonably, in order to ensure quality and improve the economic efficiency of cable operations.
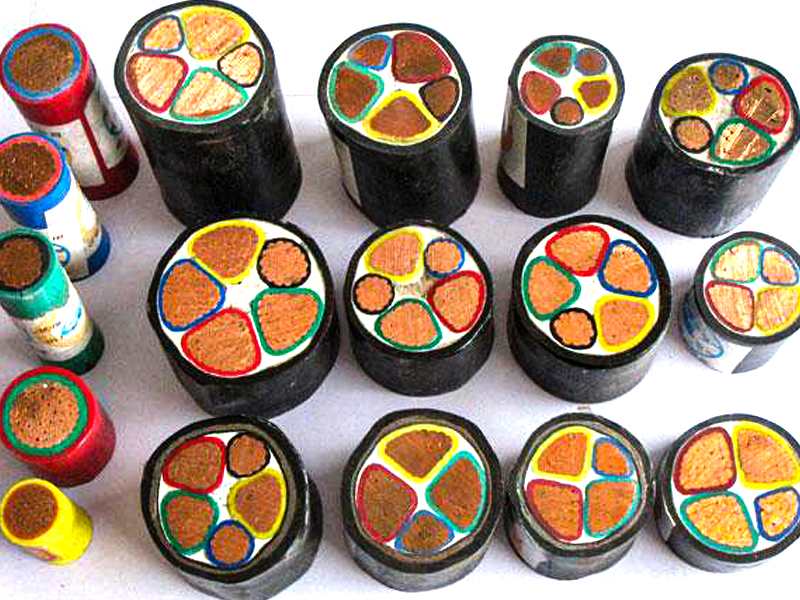

Before installation: check the low-voltage cable
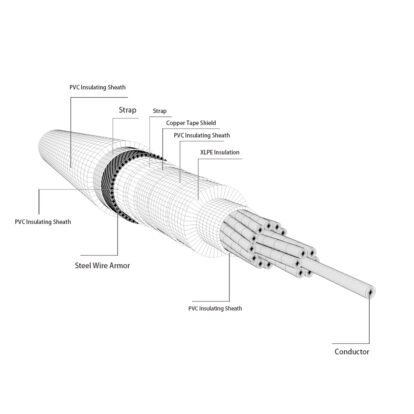
To ensure the safe and stable operation of the power network, numerous power equipment and accessories are required, among which low-voltage cables are one of the important devices. Before entering the ground for construction, it is necessary to identify and inspect the quality of the cable and its accessories, and focus on studying the key points of the installation process. In fact, most of the problems that occur during the operation of low-voltage cables and their accessories are not directly caused by factors such as excessive power load or improper installation, but rather due to the lack of strict quality standards for cables and accessories before entering the ground. Through practice, it has been found that low-voltage cables need to undergo quality checks and tests in several aspects after being purchased and transported to the construction site, such as checking the technical documents for cables and accessories to ensure their completeness, verifying the cable model, quantity, length, specifications, appearance, and whether the cable accessories are complete according to the technical documents, and ensuring the sealing of the cable end. If the sealing is not good, a cable dampness test should be carried out promptly.
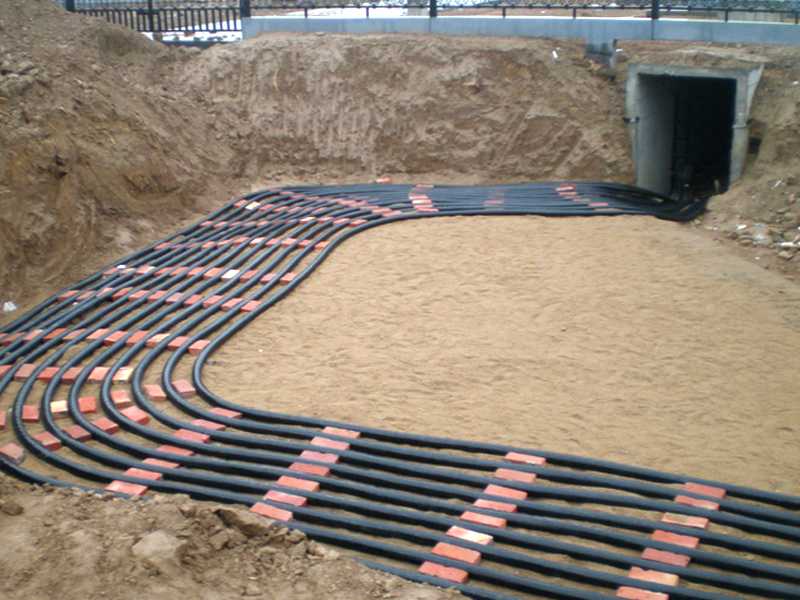

Low-voltage cable laying methods
In practice, low-voltage cables have various laying methods, and each laying method can be determined according to the scale and requirements of the cable construction project. Common low-voltage cable laying methods include directly burying the cable, laying it in a cable trench, laying it in a conduit, and laying it on a suspension system. Each laying method has its advantages, and the laying method should be chosen reasonably based on the content and requirements of the cable construction project.
Direct burial of low-voltage cables
Dig a trench with a depth of 0.8m to 1.5m and bury the low-voltage cable directly inside. This laying method is called direct burial. In general, this method is commonly used in urban public areas, such as park areas, sidewalks, etc., and can give full play to its advantages of simple and economical laying. From the advantages and disadvantages of the direct burial of low-voltage cables, this construction mode can maintain good heat dissipation of the cable, and the bending laying is more convenient. The laying cost and material consumption are minimal, and the cable line transmission capacity is large. The construction period is short, and the construction and subsequent maintenance are convenient. However, this laying method is also prone to external damage, and road excavation is required for additional installation and removal. Soil chemical reactions can damage cable components, and other defects.
The technical control points of the direct burial of low-voltage cables are as follows: Firstly, based on the cable design specifications, select the cable laying path and investigate the geological conditions of the laying area. If the soil in the section has acid-base corrosion and electrochemical corrosion, it should be avoided in advance. Secondly, the construction section is divided based on the length of one reel of cable. Thirdly, follow the construction sequence of pre-buried conduit, cable trench excavation, cable laying, fine soil covering, cover plate protection, and backfilling. After a section of laying construction is completed and cleaning measures are taken, the second section of laying construction can be carried out. Finally, pay attention to the following matters: 1) The width of the trench excavation depends on the number of cables to be laid. If only one cable is to be laid, the width should be kept between 0.4m to 0.5m. If two or more cables are to be laid, the width should be increased proportionally. If the cable needs to be bent and laid, the width at the bending point should not be less than the bending radius of the cable. 2) The trench depth must be greater than 0.9m, and the soil layer below the pavement material should be placed on both sides of the trench, with a spacing of about 0.3m.

Conduit laying of low-voltage cables
The way to set up underground pipes and lay low-voltage cables inside is called conduit laying. Conduit laying is more suitable for cable crossing areas. This method is often used in areas where excavation is difficult or traffic carrying capacity is high. The advantages of conduit laying for low-voltage cables include low mutual influence between cables, convenient addition and removal, strong load-bearing capacity, and less damage from external forces. However, it also has drawbacks such as high laying cost, easy fatigue of metal protective cover due to cable thermal expansion, easy sliding of skewed waves, poor heat dissipation, and difficult cable replacement.
The technical points of conduit laying of low-voltage cables are as follows: First, strictly follow the cable design specifications for laying operations. If there are flammable media in the laying area, conduit laying cannot be used. Second, determine the interface clearance size and elevation of the conduit according to the requirements of the cable laying project. The conduit is generally made of brick masonry. Third, a load-bearing cover plate should be set above the conduit in the driving area, and expansion joints should be made every 60m of conduit. Fourth, inspection holes for drainage should be set at about every 50 meters of conduit, and the slope of the conduit bottom should be 0.5%. Fifth, cable brackets should be installed on the inner wall of the conduit, with a spacing of 80 cm as the benchmark. Sixth, the cables and attached iron parts laid in the conduit should be treated with anticorrosion measures while being grounded. A group of grounding poles should be set every 50m. Finally, the traction force for conduit laying should be moderate and should not exceed the maximum tensile force that the cable can bear. If cable overlapping is necessary in the working well, the overlap length should be less than 1.5m.
Cable trench laying of low-voltage cables
Low-voltage cable trench laying is mainly carried out in pre-laid cable trenches. This laying method is mainly suitable for urban main roads, substation outgoing lines, parallel sections of voltage levels, or areas where multiple cables need to be laid. When cables need to be crossed, cable trench laying is also mainly used. The advantages of cable trench laying technology include low cost, small laying area, and flexible routing. It is more effective in areas where direct burial is not possible, large venues, substations, etc. However, in subsequent maintenance inspections, cover plate lifting operations are required, which is inconvenient.
The technical points of cable trench laying of low-voltage cables are as follows: First, strictly follow the cable design specifications for operations. If there are flammable media in the laying area, cable trench laying cannot be used. Second, determine the interface clearance size and elevation of the cable trench according to the requirements of the cable laying project. The cable trench is generally made of brick masonry. Third, a load-bearing cover plate should be set above the cable trench in the driving area, and expansion joints should be made every 60m of cable trench. Fourth, inspection holes for drainage should be set at about every 50 meters of cable trench, and the slope of the cable trench bottom should be 0.5%. Fifth, cable brackets should be installed on the inner wall of the cable trench, with a spacing of 80 cm as the benchmark. Sixth, cables and attached iron parts laid in the cable trench should be treated with anticorrosion measures while being grounded. A group of grounding poles should be set every 50m. Finally, use the method of pouring concrete to set the foundation.
When pouring concrete to set the foundation, it is necessary to use a rubber sealing strip or lining pad to seal the expansion joint. In addition, no matter which laying method is used for low-voltage cables, cable drainage work must be done to maintain the performance of cable components. This step mainly relies on cable layer-by-layer inspection, cable structure drainage facility design, and civil engineering quality supervision to achieve the purpose of drainage and sealing.
Conclusion
With the expansion of urban infrastructure construction, the pressure of power supply and delivery in cities has increased sharply. At the same time as fully exerting the function of substation power distribution, attention should be paid to the supporting cable laying facilities to improve the integrity of power supply. In actual construction, low-voltage cable laying methods should be reasonably selected based on the type of cable and the natural environment of the construction area to ensure that the cable effectively plays its role in power transportation and provides basic guarantee for social livelihood construction.