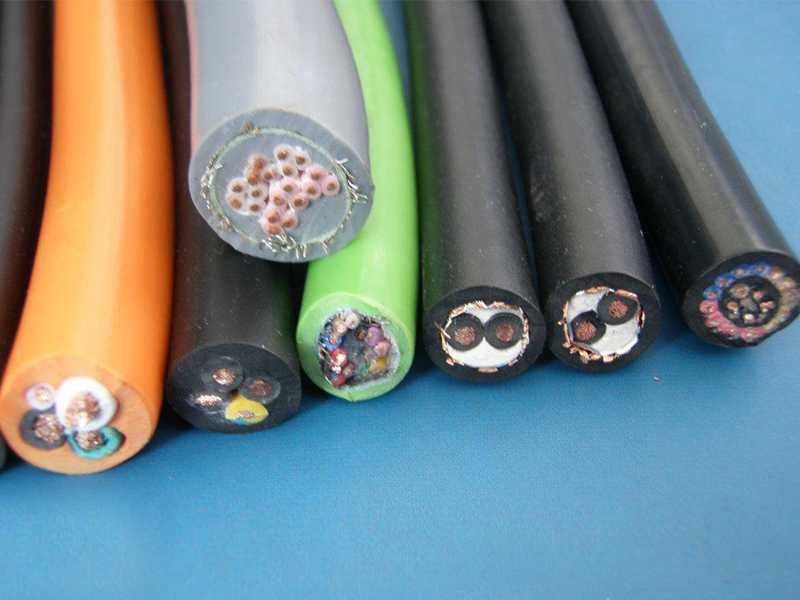
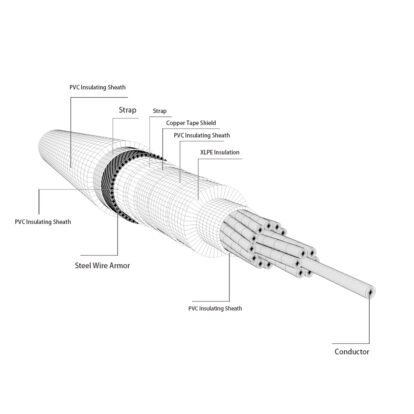
At present, the cable industry is accustomed to collectively refer to cables with certain fire resistance properties such as flame-retardant, halogen-free low-smoke or low-halogen low-smoke, and fire-resistant as fire-resistant cables. We have sorted out the specific classification standards for fireproof cables from the "Cable Application Technology Research Institute" for your reference!
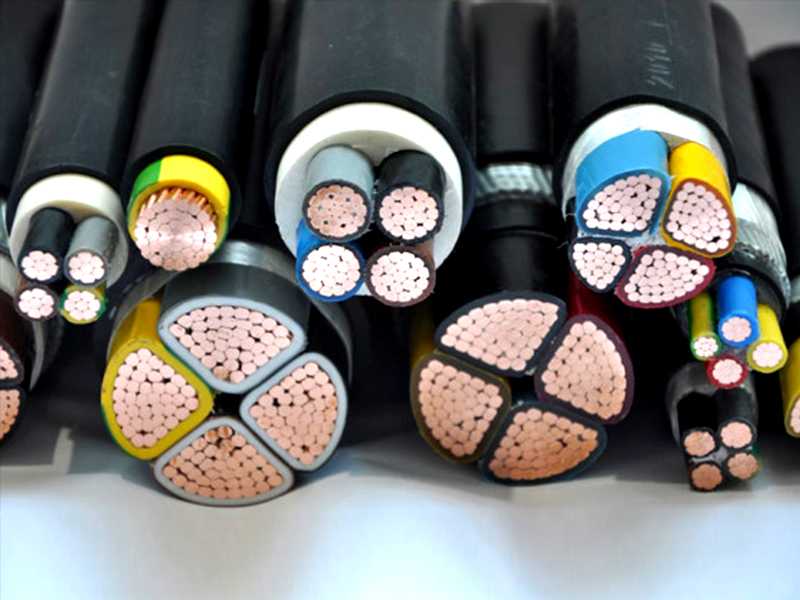

Type of flame retardant cables:
- Traditional flame retardant cables
The characteristic of flame retardant cable is to delay the spread of flame along the cable so that the fire will not expand. Because of its low cost, it is a cable variety widely used in fireproof cables. Whether it is a single cable or a bunch of laying conditions, when the cable is burned, the spread of the flame can be controlled within a certain range, so it can avoid major disasters caused by the fire and delay of the cable, thereby improving the fire protection level of the cable line . - Halogen-free low-smoke flame-retardant cable
The characteristic of the halogen-free low-smoke cable is that it not only has excellent flame retardancy, but also the material that constitutes the low-smoke and halogen-free cable does not contain halogen. , instruments and equipment damage, which is conducive to timely rescue in case of fire. Although the halogen-free low-smoke flame-retardant cable has excellent flame retardancy, corrosion resistance and low smoke concentration, its mechanical and electrical properties are slightly worse than ordinary cables. - Low-halogen, low-smoke and flame-retardant cables
The hydrogen chloride emission and smoke concentration indicators of the low-halogen low-smoke flame-retardant cable are between the flame-retardant cable and the halogen-free low-smoke flame-retardant cable. Low-halogen cables also contain halogens in their materials, but at lower levels. This cable is characterized not only by its flame retardant properties, but also by the fact that it emits less smoke and less hydrogen chloride when burned. This kind of low-halogen low-smoke flame-retardant cable is generally made of polyvinyl chloride as the base material, and then processed with high-efficiency flame retardant, HCL absorbent and smoke suppressant. Therefore, this flame-retardant material significantly improves the combustion performance of ordinary flame-retardant PVC materials. - Fire-resistant cables
The fire-resistant cable can maintain normal operation for a certain period of time under the condition of flame burning, and can maintain the integrity of the line. The fire-resistant and flame-retardant cable produces less acid gas and smoke when burning, and its fire-resistant and flame-retardant performance is greatly improved. Especially when burning, accompanied by water spray and mechanical shock and vibration, the cable can still maintain the complete operation of the line.
Flame retardant cable standards and grades
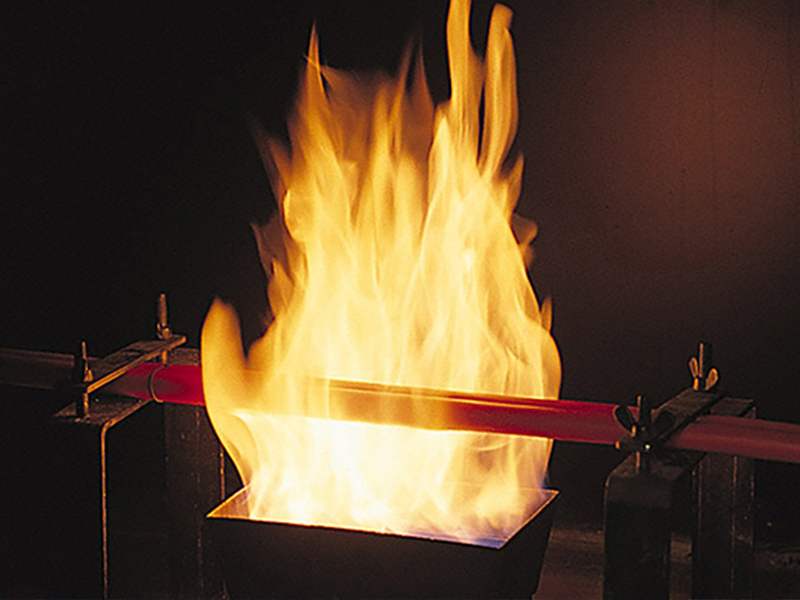

The main technical indicators of cables related to fire safety are the flame retardancy of CO2 cables, the density of smoke and the toxicity of gases. American fire protection standards focus more on the first two issues, but Europe and the United States have completely different views on fire safety. The traditional concept in the United States believes that the root of the fire is the generation of carbon monoxide poisonous gas and the heat release of CO into CO2 during the subsequent combustion process. Therefore, controlling the amount of heat release during the combustion process can reduce the hazards of the fire. Since the European tradition, it is firmly believed that the amount of halogen acid released during combustion, gas corrosiveness, smoke concentration and gas toxicity are the main factors that determine whether people can safely leave the fire scene.
1. IEC flame retardant standard
In order to evaluate the flame retardant performance of cables, the International Electrotechnical Commission has formulated three standards, IEC60332-1, IEC60332-2 and IEC60332-3. IEC60332-1 and IEC60332-2 are used to evaluate the flame retardancy of a single cable when it is laid obliquely and vertically (the domestic standards correspond to GB12666.3 and GB12666.4). IEC60332-3 (corresponding to GB12666.5-90 in China) is used to evaluate the flame retardancy of bundled cables when they burn vertically. In contrast, the requirements for the flame retardancy of bundled cables when they burn vertically are much higher. IEC60332-1/BS4066-1 flame retardant grade (single wire or cable vertical burning test: this is the flame retardant standard of a single cable. The test stipulates that a 60cm long sample is vertically fixed in an open metal box, and the flame The propane burner with a length of 175mm is in contact with the cable at an angle of 45 degrees from the position of 450mm from the upper fixed end of the sample. If the damaged part of the sample is not more than 50mm from the lower part of the fixed end, the test is passed. IEC60332-3/BS4066 -3 Flame retardant grade: This is the flame retardant standard of bundled cables. The test stipulates that the bundled 3.5m long cable samples are fixed on the trapezoidal test frame with iron wires, and the number of samples is determined according to the non-metallic materials required by different classifications. The sample is hung vertically on the back wall of the combustion furnace, and the air is introduced into the combustion furnace through the air inlet on the bottom plate. The propane plane burner contacts the sample with a flame of 750 ° C, and the sample is blown under forced air (airflow discharge 5m3/min, In the case of a wind speed of 0.9m/s), it must not ignite within 20 minutes of vertical combustion, and the cable will extinguish itself within 2.5 meters of flame spread. IEC60332 has Class A, Class B, Class C and Class D to evaluate flame retardancy Performance pros and cons.
2. UL flame retardant standard

Any cable listed by UL has been tested and verified to meet a certain fire rating, and the UL identification, fire rating and approval number can be printed on the cable.
Supercharging stage-CMP stage (supply air combustion test/Steiner air duct experiment).
This is the cable with the highest requirements in the UL fire protection standard. The applicable safety standard is UL910. The experiment stipulates that multiple samples are laid on the horizontal air duct of the device, and burned for 20 minutes with an 87.9KW gas Bunsen burner (300,000BTU/Hr). The passing criterion is that the flame does not extend beyond 5 feet from the front of the gas Bunsen burner flame. The peak value of the optical density is at most 0.5, and the average density value is at most 0.15.
This type of CMP cable is typically installed in air return plenum systems used in ventilation ducts or air handling equipment and is approved for use in Canada and the United States. FEP/PLENUM materials conforming to UL910 standard have better flame retardancy than low-smoke and halogen-free materials conforming to IEC60332-1 and IEC60332-3 standards, and the concentration of smoke when burned is lower.
3. Trunk level-CMR level (vertical combustion test)
This is a commercial-grade cable in the UL standard, and the applicable safety standard is UL1666. The experiment stipulates that multiple samples are laid on a simulated vertical shaft, and the specified 154.5KW gas Bunsen burner (527, 500BTU/Hr) is used for 30 minutes. The passing criterion is that the flame cannot spread to the upper part of the room to a height of 12 feet. There is no smoke concentration specification for trunk-level cables, and they are generally used for vertical and horizontal wiring on floors.
4. Commercial grade-CM grade (vertical burning test)
This is a commercial-grade cable in the UL standard, and the applicable safety standard is UL1581. The experiment stipulates that multiple samples are laid on a vertical 8-foot-high support, and burned (70,000BTU/Hr) for 20 minutes with a specified 20KW ribbon blowtorch. The acceptance criterion is that the flame cannot spread to the upper end of the cable and self-extinguish. UL1581 is similar to IEC60332-3C, but the number of cables laid is different. Commercial-grade cables do not have smoke density specifications, and are generally only used for horizontal wiring on the same floor, not for vertical wiring on floors.
5. General-purpose grade-CMG grade (vertical combustion test)
This is a general-purpose cable in the UL standard, and the applicable safety standard is UL1581. The test conditions of the commercial grade and the general grade are similar, and they are both approved for use in Canada and the United States. General-purpose cables do not have smoke density specifications, and are generally only used for horizontal wiring on the same floor, not for vertical wiring on floors.
6.Household level-CMX level (vertical combustion test)
This is a household-grade cable in the UL standard, and the applicable safety standard is UL1581, VW-1. The experiment stipulates that the sample should be kept vertical, and burned (30,000TU/Hr) for 15 seconds with a test blowtorch, then stopped for 15 seconds, and repeated. 5 times. The qualified standard is that the afterflame should not exceed 60 seconds, the sample should not be burned by more than 25%, and the cotton pad at the bottom should not be ignited by falling objects. UL1581-VW-1 is similar to IEC60332-1, but the burning time is different. This grade also has no smoke or toxicity specifications and is only used in home or small office systems where a single cable is run.