When most people think of aluminum, they think of something light and easy to work with. However, aluminum can also be quite strong, as demonstrated by ACSR wire. This type of wire is made up of an aluminum core with a steel reinforcement, making it an excellent choice for applications that require a high level of strength. Learn more about ACSR wire and its uses in this article.
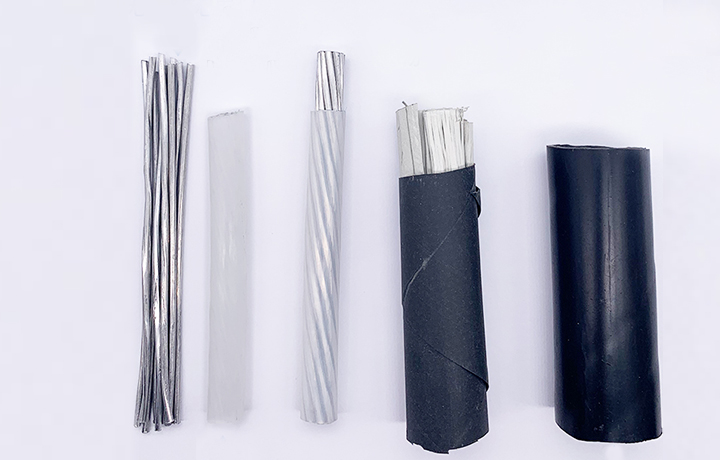

What is ACSR cable?
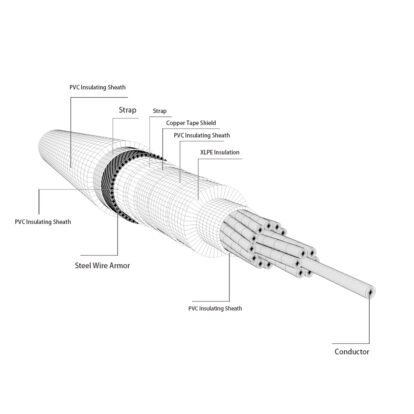
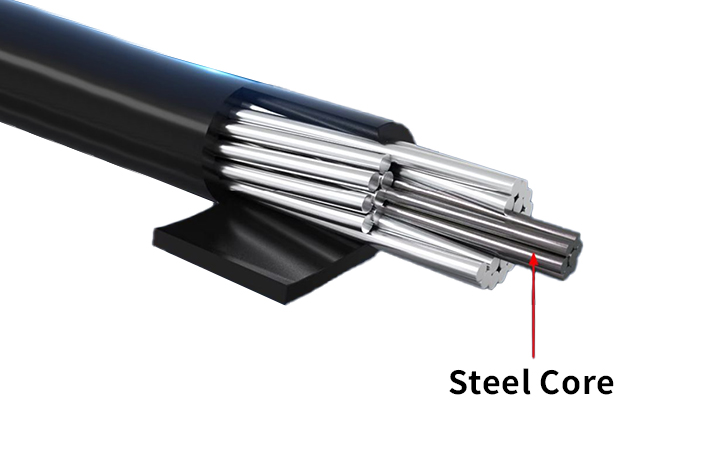
Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced is a concentrically-stranded conductor with one or more layers made of 1350-H19 aluminum wire and a core of galvanized steel wire. Depending on the size of the core, it can either be single or stranded. Steel core wire can be galvanized in either Class A, B, or Class C for corrosion protection. In addition, you can add grease to the core or infuse the complete conductor with grease for additional corrosion protection.
You can choose the proportion of steel or aluminium in an ACSR conductor based on each application's current carrying capacity and mechanical strength.
ACSR conductors have a reputation for being reliable, economical, and having a favorable strength-to-weight ratio. ACSR conductors combine the lightweight and high conductivity of aluminum with the strength and toughness of steel.
This can be used in line design to provide higher tensions, lower sag and longer span lengths than other overhead conductors. Midal can supply ACSR with non-returnable wooden/steel reels and returnable steel reels, depending on the customer's requirements.

Specifications
The aluminum core is designed to carry the electrical current, while the steel mesh provides strength and supports the weight of the conductor. The diameter of ACSR conductors can range from 6 to 18 inches (15 to 45 cm), and they are typically used in transmission lines with voltages of 138 kV or higher.
ACSR conductors are also used in some overhead power distribution lines, particularly in rural areas where the weight of the conductor is less of a concern. Thanks to its combination of lightweight and high strength, ACSR is one of the most popular choices for high-voltage transmission lines.
Features
ACSR(aluminum conductor steel reinforced) is an electrical conductor used in transmission and distribution lines. The aluminum conductor is surrounded by a layer of steel wire, which increases the strength of the conductor.
ACSR is available in different sizes, with larger sizes used for high-voltage transmission lines. The steel wires in ACSR also help to increase the conductor's resistance to bending, making it ideal for use in overhead applications. In addition, ACSR is also resistant to corrosion, making it an ideal choice for use in harsh environments.
Types of ACSR Conductors
Copper conductors were used in energy transmission for many years. However, AI conductors have now replaced them due to their low cost, high diameter, and other reasons. These ACSR conductors come in a variety of sizes.
Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced
- All Aluminium Conductor – AAC
- Aluminium Conductor Aluminium Reinforce - ACAR
- AAAC All Aluminum Alloy Conductors
Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced
ACSR conductors have steel material in them. These ACSR conductors have high strength and are suitable for installations that require extra-long spans or river crossings. They are available in a variety of tensile strengths. A high diameter can allow for a higher radiation limit.
All Aluminum Conductor (AAC).
This conductor is weaker than any other and has more sag per length. It is therefore used at the distribution level. This conductor's conductivity is slightly higher at the distribution level. Both ACSR and AAC conductors cost the same.
Aluminium Conductor Aluminium Reinforce (ACAR)
ACAR is a combination of a variety of aluminum alloy strands to provide a transmission conductor with excellent electrical and mechanical balance properties. These aluminum strands can be covered with aluminum alloy wires. The number of strands is the core of the conductor. This conductor has the main advantage of having all the strands identical. This allows for the conductor to have the best electrical and mechanical characteristics.
All Aluminium Alloy Conductors
The AAAC conductor construction looks similar to AAC but without the alloy. This conductor has the same strength as the ACSR type but is lighter due to the absence of steel. This conductor will be more expensive due to the existence of alloy formation. Because AAAC has a stronger tensile force than AAC, AAAC can be used for longer spans.
It is used in river crossing distribution levels. Comparing to AAC, this conductor has a lower sag. AAAC conductors weigh less, making them suitable for transmission and sub-transmission where a less weight support structure like mountains or swamps is required.
How do you install ACSR cable, and what safety precautions should be taken?
Installing an ACSR (aluminum conductor, steel reinforced) cable requires special care and attention to detail. This type of cable is used for high-voltage power transmission, and even a tiny mistake can result in serious damage or injury.
The first step is to determine the route the cable will take and clear any obstacles. Once the path is clear, the next step is to string the cable between poles or towers. Next, the cable must be securely fastened at each support using clamps or guy wires.
Finally, the ends of the cable must be connected to the power source. Throughout the entire process, it is important to take precautions against electrical shock. Materials such as rubber gloves and insulating tape should be used when working with the cable. By following these steps, you can safely install an ACSR cable.
What common problems with ACSR cables, and how can they be avoided or fixed?
ACSR cables are an essential part of any electrical grid, but they can also be one of the most vulnerable parts of the system. One common problem is known as "cable sag." This occurs when the weight of the cable causes it to droop, creating tension and strain on the wires.
Cable sag can be prevented by using stronger and more supportive materials, such as guy wires or reinforced concrete. Another problem that can affect ACSR cables is corrosion. This happens when the cable's steel core begins to rust, weakening the structure and making it more susceptible to damage.
Corrosion can be avoided by using a corrosion-resistant coating or by regularly inspecting and repairing any damaged areas. However, with proper maintenance, ACSR cables can play a vital role in keeping the electrical grid running smoothly.
How is ACSR cable made, and what are its components?
Aluminum conductor steel-reinforced cable, or ACSR, is a high-voltage transmission cable used in grid applications. It is made up of a core of aluminum wires surrounded by a steel wire mesh. The aluminum core is made up of several smaller wires that are twisted together. The steel wire mesh helps to provide strength and support to the cable.
The core and the surrounding steel mesh are then encased in a plastic sheath. This type of cable is used in high-voltage transmission lines because it is able to carry a large amount of current without being damaged by the heat generated by the current flow.

What are the Properties of ACSR
Skin Effect
The skin effect can reduce the conductor's cross-sectional area by reducing its current flow. AC can flow most of its current between the outer and the deeper layers of the skin. It all depends on the frequency of current flow and conductor properties.
The conductor's cross-sectional area and resistance will be reduced, resulting in higher resistance. Because the conductor's exterior is covered in aluminum, the skin effect aids its design. The ASTM, American Society for Testing & Materials standard, measures the resistance of the conductor's AC & DC to demonstrate this effect.
Hysteresis Loss
The atomic dipoles in the steel core are the main cause of hysteresis loss in the ACSR conductor. These losses aren't attractive, but they can be reduced by using aluminium layers that are located in an even place within the conductor.
This conductor, which includes no. Aluminium layers. These conductors include an odd number. An odd number of layers of aluminum is used to calculate the AC resistance. However, a magnetization feature can be used. An odd-layer design will have a lower capacity rating due to the high hysteresis loss in the steel and associated core heating. Partridge is the only ACSR conductor that has a single layer. This means that the hysteresis losses cannot be avoided.
The proximity effect
The AC current flows through conductors, and then the current flow can be reduced to smaller areas. This is known as the proximity effect.
This is due to electromagnetic induction, which creates a magnetic field that controls the flow of electricity in conductors. For example, AC supplies AC to an isolated conductor and then creates an alternating magnetic field. The magnetic field can generate eddy currents in contiguous conductors, which will change the current distribution.