- Products made of bare wire and bare conductor Pure conductor metal, without insulation or a sheath layer, as in steel-cored aluminum stranded wire, copper-aluminum busbar, electric locomotive wire, etc., are the key characteristics of this type of product. The primary production method is also a feature. Pressure processing includes smelting, calendering, drawing, compression stranding, and other processes. Suburban areas, rural areas, user main lines, switch cabinets, etc. are where the goods are most commonly utilized.
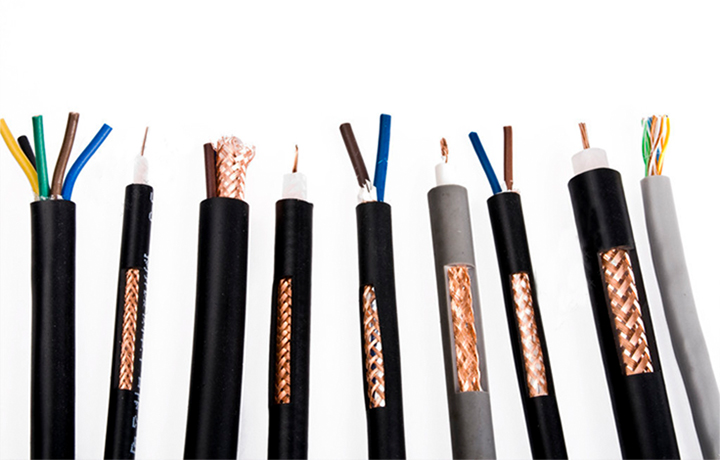
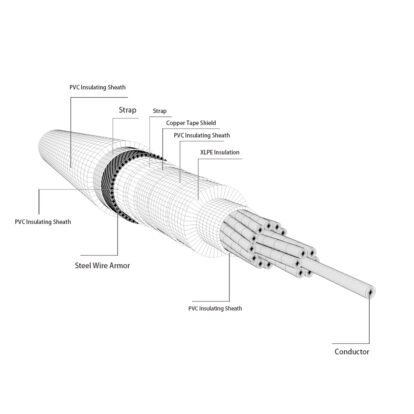
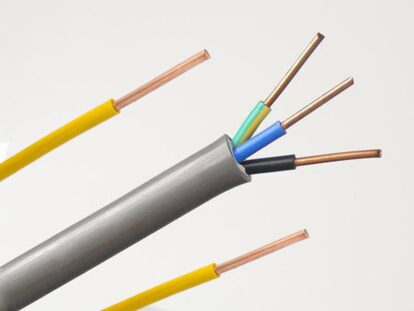
- The overhead insulated cable, overhead insulated cables with more than two cores, or twisting multiple cores (corresponding to the phase wire, neutral wire, and ground wire of the power system) are examples of this type of power cable. Other examples include adding a sheath layer to plastic or rubber-sheathed wire and cable. Drawing, stranding, insulation extrusion (wrapping), cable shaping, armoring, sheath extrusion, etc. are the primary process technologies. There are certain changes when diverse products are combined with various methods.
- Telephone wires and optical fibers (brief introduction) In the past 20 years, the communication sector has grown incredibly quickly, and the same can be said for the goods. thousands of pairs of voice cables, coaxial cables, optical cables, data cables, and even integrated communication connections have replaced the old, straightforward telephone and telegraph wires.
- New Products and Derivatives of Wire and Cable.The main drivers of derivatives and new wires and cable products are the demands of various application scenarios, application requirements, equipment convenience, equipment cost reduction, etc., as well as the adoption of new materials, special materials, product structure changes, improved process requirements, and other factors. Products from many categories are mixed.